Low noise amplifier is a key component in RF/microwave systems, mainly used to amplify weak signals while minimizing additional noise. Its core functions and application scenarios are as follows:
Core Functions:
1. Signal amplification
Enhance the amplitude of weak signals received by antennas or sensors to ensure effective processing by subsequent circuits such as mixers and ADCs.
2. Noise suppression
By optimizing the design and using low-noise materials, the self introduced noise figure (NF) is controlled within the range of 0.5-3dB (ideal amplifier NF = 0dB).
Application Scenarios:
1. Radar system
In military radar (such as airborne fire control radar) and civilian radar (such as automotive millimeter wave radar), LNA is used to amplify the weak echo signal (signal-to-noise ratio SNR < 0dB) reflected by the target. When passing through an amplification link with NF < 2dB, the radar can recognize targets with farther or lower RCS (radar cross section).
2. Wireless communication system
Low noise amplifier is the core component of 5G/6G base stations, satellite communications, and mobile terminal receiving links. It is responsible for low-noise amplification (NF < 1.5dB) of weak RF signals (as low as -120dBm) captured by the antenna before signal demodulation, significantly improving the system's receiving sensitivity. For example, in the millimeter wave frequency band (24 - 100GHz), LNA can compensate for up to 20dB of path loss, ensuring the stability of high-speed data transmission.
3. High precision testing instrument
In devices such as spectrum analyzers and vector network analyzers (VNA), LNA directly determines the instrument's noise performance and dynamic range. LNA can improve instrument sensitivity by amplifying the nV level measured signal to the effective quantization range of ADC (such as 1Vpp). Meanwhile, ultra-low noise coefficient (NF < 3dB) can effectively reduce measurement uncertainty and minimize measurement errors.
4. Expand application areas
Radio astronomy: The FAST telescope relies on liquid helium cooled LNA (NF ≈ 0.1dB) to capture 21cm spectral lines in the universe.
Quantum computing: Amplifying μV level signals (4 - 8GHz) of superconducting qubits requires near quantum limit noise performance.
Medical imaging: MRI equipment enhances μV level nuclear magnetic resonance signals through non-magnetic LNA, with a signal-to-noise ratio improvement of more than 10dB.
Qualwave Inc. provide low-noise amplifiers ranging from 9kHz to 260GHz, with a noise figure as low as 0.8dB.
The QLA-9K-1000-30-20 model, which is specially designed for scientific research and communication applications, achieves an excellent performance balance of 30dB gain and 2dB noise figure in the 9kHz~1GHz frequency band.
1. Electrical Characteristics
Frequency: 9K~1GHz
Gain: 30dB min.
Output Power (P1dB): +15dBm typ.
Output Power (Psat): +15.5dBm typ.
Noise Figure: 2dB max.
VSWR: 2 max.
Voltage: +12V DC typ.
Impedance: 50Ω

2. Absolute Maximum Ratings*1
RF Input Power: +5dBm typ.
[1] Permanent damage may occur if any of these limits are exceeded.
3. Mechanical Properties
RF Connectors: SMA female
4. Outline Drawings
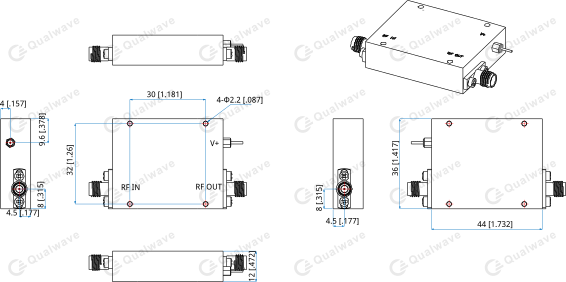
Unit: mm [in]
Tolerance: ±0.5mm [±0.02in]
5. How To Order
QLA-9K-1000-30-20
If you are interested in this product, please feel free to contact us. We are happy to provide more valuable information.
Post time: Jun-26-2025
 +86-28-6115-4929
+86-28-6115-4929